INTRODUCTION:
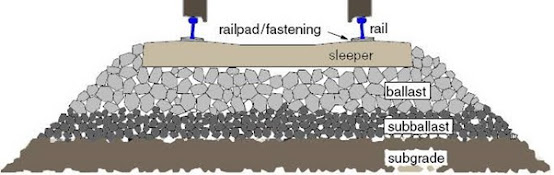
Sleepers are laid transverse to the rails on which the rails are supported and fixed. They transfer the loads from rails to the ballast and subgrade below.
FUNCTIONS OF SLEEPERS:
·
Holds the rails to maintain correct gauge.
·
Holds the rails in proper level or transverse tilt.
·
Distribute the load from the rails to ballast.
·
Provides longitudinal and lateral stability.
·
Provides means to rectify track geometry during
service life.
REQUIREMENTS OF SLEEPERS:
v
It’s is Economical.
v
It’s Moderate weight.
CLASSIFICATION OF SLEEPERS:
v
Wooden Sleepers
v
Metal Sleepers
ü Cast
Iron Sleepers
ü Steel Sleepers
v
Concrete Sleepers
ü Reinforced
concrete sleepers
ü Prestressed
concrete sleepers
WOODEN SLEEPERS:
v It’s
required for an ideal sleeper
v The
sleeper is depend upon their ability to resist the wear,decay,attack by vermin
v The
quality of timber is used in the sleeper
METAL SLEEPERS :
CAST IRON
SLEEPERS:
In
the cast iron sleepers there are five types:
·
Plot or bowl sleeper
·
Plate sleeper
·
Box sleeper
·
CST-9 Sleeper
· Rail free duplex sleeper
PLOT OR BOWL SLEEPER:
v
They consist of two bowls or plots and placed in the
ballast
ü The
Bearing area is 0.232sq.m under each rail support
PLATE SLEEPER
ü It’s
consists of rectangular plates about 86.5cm side is parallel to the rails
ü The
position of plate is held in tie bars
BOX SLEEPER
Ø Out
of use these days
CST-9 SLEEPER
Ø The
weight of broad gauge tracks consists of 230kg
It’s is easily assembled and dismantled
v
SLATE SLEEPERS:
ü These are inverted in channel folded ends
REQUIREMENTS:
·
Should maintain perfect gauge
·
Should have sufficient bearing area
SLEEPERS ADVANTAGES:
·
Easily available
·
In design the fitting are very simple
· Economical.
SLEEPERS DISADVANTAGES:
ü Alignment
maintenance are very difficult
ü Maintenance cost
is very high
ü Track
is easily disturbed
v DESIGN
CONSIDERATIONS:
Material
Selection:
Sleepers
should be in the environment and load condition
Spacing
:
It’s is
efficient and load distribution and stability
Size
and shape :
Sleepers in
the rail ballast depth
INNOVATIONS
IN SLEEPERS:
v
Advanced materials:
Fiber reinforced polymers and
recycled plastics
Improved designs:
Shapes are in better
performance
v
POINT IN SLEEPERS ARE OFTEN USED IN:
1. Rail track turnouts
2. Crossings
3. Junctions
4. Bridge approaches
CONCLUSION:
Ø Sleepers
ensure the stability, safety and durability of infrastructure about proper design.
Ø Rail
track stability and smoothness
Ø Load
distribution and transfer
Ø Prevention
of settlement and erosion
Ø Extension of infrastructure lifespan
Sleepers are a fundamental component of civil engineering projects, requiring, careful consideration and ensure optimal performance and safety.
Author
Bios:
Mr. D. Dhavashankaran, AP/Civil
Dr. N. Sridhar, AP/Civil
S. Sri Dhatchayini, III
Year / Civil
S. Vinothini, III
Year / Civil


Comments
Post a Comment