Introduction:
In recent years, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has emerged as a transformative solution for addressing healthcare challenges in rural areas, particularly through the development of portable diagnostic and medication systems. These systems are designed to enhance access to essential medical services, ensuring that underserved populations receive timely care and improved health outcomes. The need for such innovations stems from the limited access to healthcare facilities in rural regions, where residents often face significant barriers to receiving medical attention due to long distances and inadequate infrastructure. Chronic disease management is particularly challenging, as patients require consistent monitoring and medication, which can be difficult without nearby healthcare providers.
Portable diagnostic systems utilizing IoT technology offer real-time health monitoring, enabling continuous tracking of vital signs and health metrics from the comfort of patients’ homes. These systems collect and analyze data on various health parameters, providing valuable insights into patient health trends. Additionally, telemedicine capabilities allow for remote consultations with healthcare professionals, reducing the need for patients to travel long distances for routine check- ups. Key components of these systems include wearable devices, mobile health applications, portable diagnostic tools, and cloud-based data storage solutions. Wearables monitor vital signs, while mobile apps facilitate communication between patients and providers, ensuring that individuals remain engaged in their health management.
The benefits of implementing IoT in rural healthcare are numerous. Increased accessibility to medical care enables patients to adhere to treatment plans more effectively, while cost savings are achieved by minimizing the need for physical consultations. Moreover, when patients have access to real-time data and communication tools, they are more likely to take an active role in managing their health. However, challenges remain, including connectivity issues, data privacy concerns, and the need for seamless integration with existing healthcare systems. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful implementation of IoT solutions in rural healthcare settings.
Objectives:
- The system aims to enhance healthcare accessibility for rural populations through portable diagnostic tools and remote consultations.
- It seeks to facilitate real-time health monitoring and improve chronic disease management by providing regular check-ups and medication reminders.
- The objective is to reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for in-person visits and promoting preventive care through early detection of health issues.
- The system is designed to empower patients by promoting engagement and providing access to real-time health data and communication tools.
- It aims to enhance communication and collaboration among patients, healthcare providers, and specialists to ensure coordinated care.
- The objective is to utilize health data for insights that inform treatment decisions and improve overall health outcomes in the community.
- The system will ensure data security and privacy while fostering community health education through resources and training for patients and healthcare workers.
- Finally, it aims to promote scalability and sustainability, allowing for expansion to additional rural areas and adapting to technological advancements.
Methodology for the System :.
1. Needs Assessment
Conduct surveys and interviews with rural communities to identify specific healthcare challenges and needs. Analyze existing healthcare infrastructure and resources in the target areas.2. System Design
Define the system architecture, including hardware (wearable devices, portable diagnostic tools) and software (mobile applications, cloud storage). Ensure the design is user-friendly and accessible for patients with varying levels of technological proficiency.3. Technology Selection
Choose appropriate IoT devices and platforms that meet the requirements for data collection, transmission, and analysis. Evaluate options for secure cloud storage and data management solution4. Prototype Development
Develop a prototype of the portable diagnostic and medication system, integrating selected hardware and software components. Conduct initial testing to ensure functionality and reliability.5. Pilot Testing
Implement a pilot program in a selected rural community to evaluate the system’s effectiveness and gather user feedback. Monitor system performance, user engagement, and health outcomes during the pilot phase.6. Data Collection and Analysis
Collect data on patient health metrics, system usage, and user satisfaction throughout the pilot program. Analyze the data to assess the impact of the system on healthcare access and patient outcomes.7. Training and Support
Provide training sessions for healthcare providers and patients on how to use the system effectively. Establish ongoing technical support to address any issues that arise during implementation.8. Evaluation and Feedback
Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the pilot program, including qualitative and quantitative assessments. Gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and potential enhancements.9. System Refinement
Based on evaluation results and user feedback, refine the system to address any identified issues and improve functionality. Update training materials and support resources as needed.10. Full-Scale Implementation
Roll out the refined system to additional rural communities, ensuring adequate resources and support are in place. Monitor the implementation process and continue to collect data for ongoing evaluation.11. Sustainability Planning
Develop a plan for the long-term sustainability of the system, including funding, maintenance, and community engagement strategies. Explore partnerships with local healthcare organizations and government agencies to support ongoing operations.12. Continuous Improvement
Establish a framework for continuous monitoring and improvement of the system based on evolving healthcare needs and technological advancements. Regularly update the system and training programs to incorporate new features and best practices.Proposed Framework of System:
Circuit Diagram:
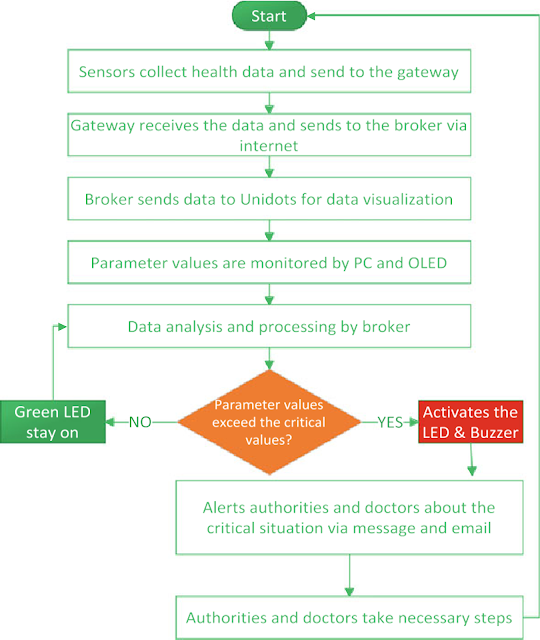
Flow Chart for the Proposed System :
Advantages:
- Increased Accessibility
- Real-Time Health Monitoring
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Enhanced Patient Engagement
- Remote Consultations
- Data Collection and Analysis
- Improved Chronic Disease Management
- Integration with Mobile Health Applications
- Cloud-Based Data Storage
- Scalability
Conclusion:
Author Bios
1. Mr. Bashkaran K, AP / BME
2. Mr.Ragul Kannan R, AP / BME
3. Vishnu G, IV-Year / BME
4. Sridharan P, IV-Year / BME


Comments
Post a Comment